
Since you cannot say exactly how much each income differs from the others in your data set, you can only order the income levels and group the participants. Ratio level: You collect data on the exact annual incomes of your participants.Īt a ratio level, you can see that the difference between A and B’s incomes is far greater than the difference between B and C’s incomes.Īt an ordinal level, however, you only know the income bracket for each participant, not their exact income.The brackets are coded with numbers from 1–3. You ask participants to select the bracket that represents their annual income.

Example of a variable at 2 levels of measurementYou can measure the variable of income at an ordinal or ratio level. In many cases, your variables can be measured at different levels, so you have to choose the level of measurement you will use before data collection begins. The different levels limit which descriptive statistics you can use to get an overall summary of your data, and which type of inferential statistics you can perform on your data to support or refute your hypothesis. The level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. In ratio scales, zero does mean an absolute lack of the variable.įor example, in the Kelvin temperature scale, there are no negative degrees of temperature – zero means an absolute lack of thermal energy. You can categorize, rank, and infer equal intervals between neighboring data points, and there is a true zero point.Ī true zero means there is an absence of the variable of interest. A zero on a test is arbitrary it does not mean that the test-taker has an absolute lack of the trait being measured. The same is true for test scores and personality inventories. But zero degrees is defined differently depending on the scale – it doesn’t mean an absolute absence of temperature. The difference between any two adjacent temperatures is the same: one degree. You can categorize, rank, and infer equal intervals between neighboring data points, but there is no true zero point.
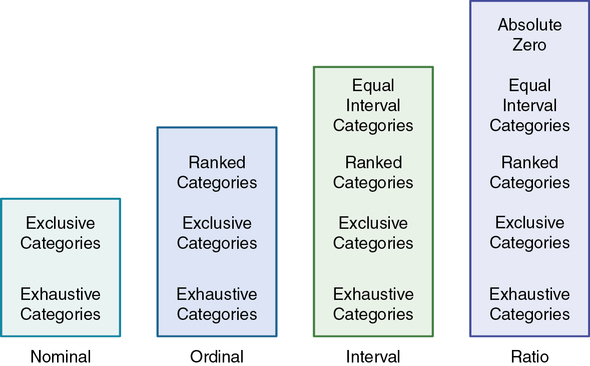
Going from lowest to highest, the 4 levels of measurement are cumulative. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio data

Frequently asked questions about levels of measurement.Quiz: Nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio?.Which descriptive statistics can I apply on my data?.Why are levels of measurement important?.Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
